Forms of Carbon
There are many forms of carbon, including fullerenes and nanotubes.
Fullerenes NanotubesX
Type of structure
A fullerene is a carbon structure made of hollow carbon molecules that form a closed sphere. This sphere that resembles a soccer ball (technically, it is a truncated icosahedron). It consists of 20 hexagonal and 12 pentagonal rings. They are also known as buckminsterfullerenes, named after Buckminster Fuller, who designed geodesic domes. The first fullerene, C60 (named because it had 60 carbon atoms) was discovered in 1985 by Sir Harold W. Kroto, Robert F. Curl and Richard E. Smalley.
How carbon atoms bond with one another
As it has 4 electrons, carbon does not form ionic bonds, only covalent bonds. It can form single, double, and triple bonds.
Each carbon in a fullerene is bonded to three other carbon atoms in a covalent bond.
Strength of bond
A fullerene and nanotube bond is a carbon double bond and the strength of its bond is 614 (kJ/mol) and its bond length is 134 (pm). Nanotubes are so highly resistant to tension that to they could justly be called superstrings.
Example
Buckyballs are an example of Fullerenes. Buckyballs are the smallest fullerene molecule containing pentagonal and hexagonal rings. There are many types of buckyballs, such as boron buckyballs, that use boron atoms instead of carbon, and are much more stable than with carbon atoms.
Close
X
Left, a picture of carbon nanotubes taken with a scanning tunneling microscope; Right, a helically coiled carbon nanotube
Type of structure
Nanotubes, a type of fullerene, were first made in 1991. They are light, flexible and extremely strong. Although they look like black soot, they are actually good conductors of thermal energy (heat) and electricity. Because of this, they work well as semiconductors and could replace silicon in many devices. A carbon nanotube is a tiny, hollow cylinder structure. The wall of a nanotube is made of a one-atom-thick sheet of carbon, called graphene.
How carbon atoms bond with one another
As it has 4 electrons, carbon does not form ionic bonds, only covalent bonds. It can form single, double, and triple bonds. The carbon atoms in a nanotube are arranged in many hexagons and are connected through covalent bonds. Since they are hexagons, each carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atoms.
Strength of bond
A fullerene and nanotube bond is a carbon double bond and the strength of its bond is 614(kJ/mol) and its bond length is 134(pm). Nanotubes are so highly resistant to tension that to they could justly be called superstrings.[]
Example
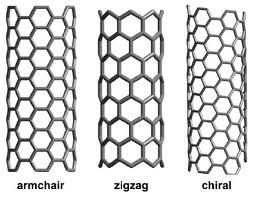
An example of a nanotube is a zigzag. A zigzag nanotube has a distinct zigzag pattern that differentiates it from other types of nanotubes like armchair and chiral.
Close
(c) 2016. Coded with <3 by Olivia Chang.
